Peripheral Neuropathy
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy, commonly known as simply Diabetic Neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can occur in individuals with diabetes. This condition affects the peripheral nervous system, which is responsible for transmitting messages from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body.
Diabetic Neuropathy can lead to many symptoms, including numbness, tingling, pain in the hands and feet, muscle weakness, and difficulty with coordination. In some cases, this condition can be severe enough to impact an individual’s quality of life and ability to perform daily activities. In this context, it is crucial to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for Diabetic Neuropathy.
What is Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy (DPN) is a type of nerve damage that occurs in people with diabetes, mainly those who have had the condition for a long time or have poorly controlled blood sugar levels. DPN affects the peripheral nerves, which are the nerves that connect the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body, such as the arms, legs, hands, and feet. It can cause various symptoms that vary in severity and impact a person’s quality of life.
DPN can present itself in different ways, such as numbness, tingling, burning, or stabbing pain, particularly in the feet and legs. Some people may also experience weakness, clumsiness, or a loss of balance. DPN can be particularly dangerous for people with diabetes as they may not feel pain or injuries in their feet or legs, which can lead to ulcers or infections. In severe cases, DPN can cause muscle weakness and even paralysis. Therefore, it is essential to manage diabetes and prevent or delay the onset of DPN.
Signs of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
DPN can manifest in different symptoms, and some of the common signs of DPN include:
- Numbness or reduced sensation in the feet or hands
- Tingling or burning sensation in the feet or hands
- Sharp or shooting pain in the feet or hands
- Muscle weakness and difficulty in walking or standing
- Poor coordination and balance
- Sensitivity to touch or pressure
- Cramping or twitching of muscles
- Changes in the shape of feet or toes
- Skin changes, such as dry skin or cracking
- Slow healing of wounds or sores on the feet or hands.
Symptoms of DPN can vary from person to person and range from mild to severe. Some people with DPN may experience only one or two symptoms, while others may have multiple symptoms.
Symptoms of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Here are some common symptoms of DPN:
- Tingling or numbness in the hands, feet, or legs
- Burning pain
- Sharp or jabbing pain
- Extreme sensitivity to touch
- Muscle weakness
- Loss of balance or coordination
- Loss of reflexes
- Difficulty walking or performing other physical activities
- Changes in skin, hair, or nails
- Changes in the foot’s shape include flat feet or claw toes.
These symptoms can vary in severity and be felt in different body parts. Not everyone with DPN will experience all of these symptoms, and some people may not experience any symptoms at all.
What Causes Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
High blood sugar levels cause DPN over an extended period. The excess sugar in the blood can damage nerves throughout the body, particularly in the feet and legs. The damage to the nerves disrupts their normal functioning and interferes with brain and body communication. Over time, this damage can lead to various symptoms and complications associated with DPN.
Not all people with diabetes will develop DPN. However, those who have poorly controlled blood sugar levels or have had diabetes for an extended period are at a higher risk of developing the condition. Other risk factors for developing DPN include obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and smoking.
It is also believed that genetic factors may play a role in the development of DPN. Some people may have a genetic predisposition to developing nerve damage, which makes them more susceptible to the effects of high blood sugar levels. Other medical conditions, such as kidney disease or autoimmune disorders, can also contribute to the development of DPN.
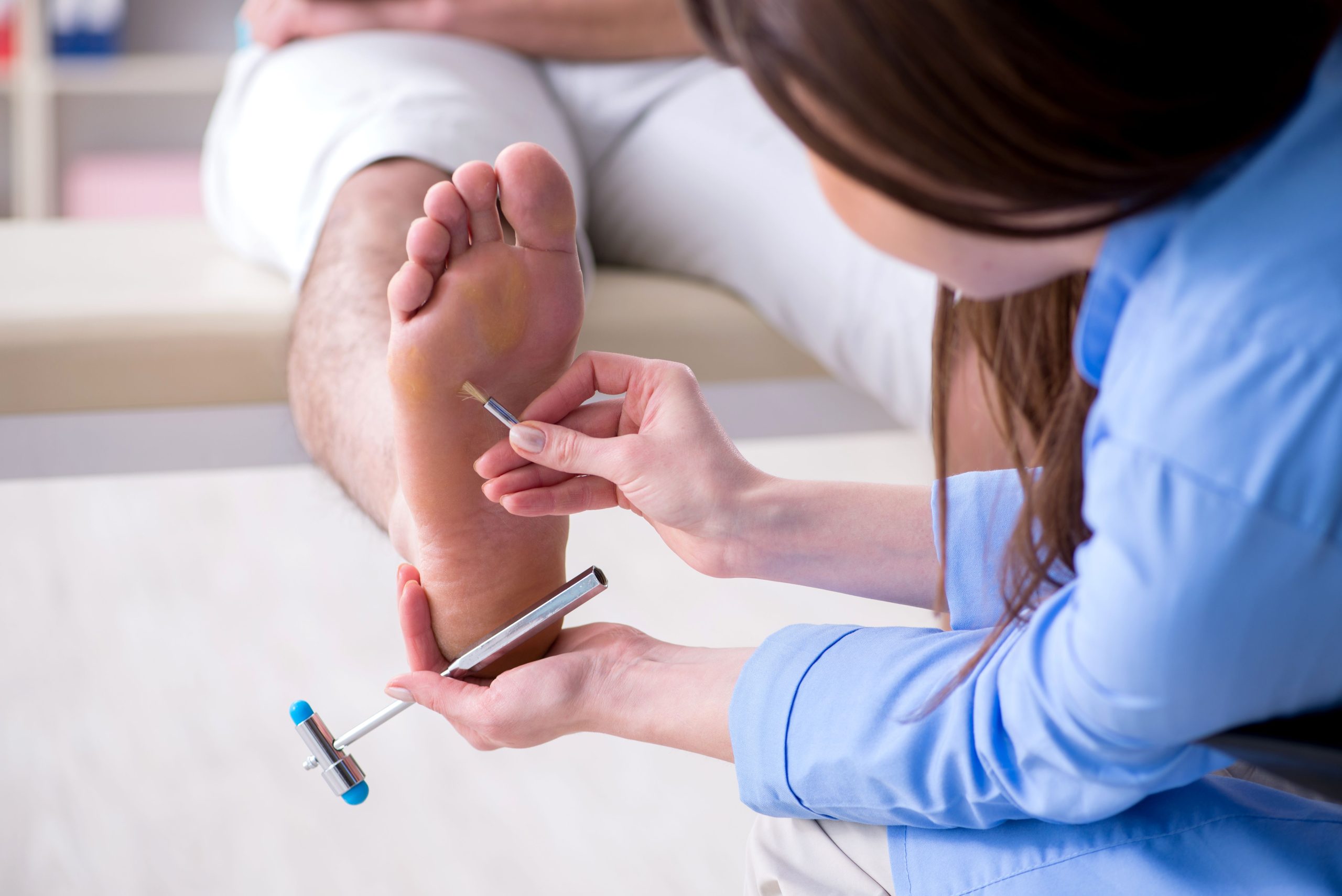
More Risk Factors for Developing DPN
The following are some risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing DPN:
- Poor Blood Sugar Control: People with poorly controlled diabetes are at higher risk for DPN. When blood sugar levels are consistently high, it can damage the nerves throughout the body, including the peripheral nerves.
- Length of Time with Diabetes: The longer a person has diabetes, the greater their risk of developing DPN because nerve damage can occur over time due to high blood sugar levels.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the nerves, increasing the risk of DPN.
- High Blood Pressure: High blood pressure can damage blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the nerves, increasing the risk of DPN.
- High Cholesterol: High cholesterol can also damage blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the nerves, increasing the risk of DPN.
- Being Overweight or Obese: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing DPN. Being overweight can increase the DPN risk because excess weight can pressure the nerves, damaging them over time.
- Genetics: Some people may be genetically predisposed to developing DPN. A person with a family history of the condition may be at higher risk for developing it themselves.
- Age: As people age, their risk of developing DPN increases. As people age, nerve damage can occur over time, and the body may become less able to repair damaged nerves.
- Gender: Men are more likely than women to develop DPN.
- Kidney Disease: People with kidney disease are at higher risk for developing DPN. People with kidney disease are at higher risk because kidney disease can damage nerves and reduce blood flow to the nerves.
- Alcohol Consumption: Drinking too much alcohol can damage nerves, increasing the risk of DPN.
Having one or more of these risk factors does not mean that a person will definitely develop DPN. However, if a person is at higher risk, they should take steps to manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk factors to help prevent or delay the onset of DPN.
Complications of DPN
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy (DPN) is a condition that can lead to several complications affecting various parts of the body. Here are some of the most common complications of DPN:
Foot Ulcers and Infections
Foot ulcers and infections are common complications of diabetic peripheral Neuropathy (DPN). DPN can cause nerve damage, leading to a loss of sensation in the feet. This loss of sensation makes it difficult for people with DPN to feel injuries to their feet, such as cuts, blisters, or sores. If left untreated, these injuries can develop into foot ulcers and become infected, leading to severe complications.
Foot ulcers are open wounds that develop on the feet. They often occur on the bottom of the foot or the toes. Various factors, including pressure from shoes, cuts or injuries to the foot, and poor circulation, can cause foot ulcers. People with DPN are at higher risk of developing foot ulcers because they may not be able to feel when their feet are injured.
If a foot ulcer becomes infected, it can lead to a more severe condition called cellulitis. Cellulitis is a bacterial infection of the skin and the tissues beneath the skin. Symptoms of cellulitis include redness, swelling, warmth around the affected area, fever, and chills. If left untreated, cellulitis can spread to other parts of the body and lead to life-threatening sepsis.
Preventing foot ulcers and infections in people with DPN is vital to avoid serious complications. Here are some steps that people with DPN can take to prevent foot ulcers and infections:
- Check Feet Regularly: People with DPN should check their feet daily for cuts, sores, or other injuries. If they cannot do this, a caregiver or healthcare provider should check their feet regularly.
- Wear Appropriate Shoes: Shoes that fit well and provide adequate support can help prevent foot injuries. People with DPN should avoid shoes that are too tight or too loose.
- Keep Feet Clean and Dry: Washing feet daily with warm water and mild soap, and drying them thoroughly afterward, can help prevent infections.
- Trim Toenails Carefully: People with DPN should trim them carefully to avoid injuring the skin around the nails.
- Manage Blood Sugar Levels: Keeping blood sugar levels under control can help prevent nerve damage and reduce the risk of foot ulcers.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the feet, increasing the risk of foot ulcers and infections.
- Get Regular Foot Exams: People with DPN should have regular foot exams by a healthcare provider to check for any signs of foot ulcers or infections.
If a foot ulcer or infection does develop, it is crucial to seek prompt medical treatment to avoid serious complications. Treatment may include antibiotics to treat the condition, wound care to help the ulcer heal, and measures to relieve pressure on the affected area. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged tissue or prevent the infection from spreading.
Charcot Joint
The Charcot joint, also known as neuropathic arthropathy, affects the joints in the foot and ankle. Charcot joint occurs when the bones weaken and break down due to nerve damage, which can cause the joint to become deformed and unstable. This condition can lead to a loss of mobility and function in the affected joint.
Charcot joint can be difficult to diagnose because the symptoms may be mistaken for other conditions, such as gout or rheumatoid arthritis. The most common signs of the Charcot’s joint include redness, swelling, warmth around the affected joint, and a loss of sensation or feeling in the foot or ankle. As the condition progresses, the joint may become deformed and unstable, and it may be difficult to bear weight on the affected foot.
Muscle Weakness and Atrophy
DPN can cause nerve damage that affects the arms, legs, and feet muscles, leading to weakness and a loss of muscle mass. Muscle weakness in DPN patients can manifest in several ways. Some people may experience difficulty walking, standing, or maintaining balance due to weak leg muscles. Others may have trouble gripping objects or performing fine motor tasks due to hand and finger weakness.
Atrophy, or a loss of muscle mass, can also occur in DPN patients. Loss of muscle mass can lead to decreased muscle strength and mobility. Atrophy in the legs can make it difficult to walk or stand, while atrophy in the hands can make it difficult to perform everyday tasks.
The causes of muscle weakness and atrophy in DPN patients are not fully understood. However, it is thought that nerve damage may lead to decreased blood flow to the muscles, which can cause them to weaken and atrophy over time.
Treatment for muscle weakness and atrophy in DPN patients may involve physical therapy and exercise to improve muscle strength and mobility. People with DPN may also benefit from assistive devices, such as canes or walkers, to help them maintain their balance and prevent falls. Medication may sometimes be prescribed to help manage symptoms such as pain or muscle spasms.
Autonomic Neuropathy
Autonomic Neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that affects the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary functions such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing. Autonomic Neuropathy is a common complication of DPN, as high blood sugar levels can damage the nerves that control these functions.
Symptoms of Autonomic Neuropathy can vary depending on which functions are affected. Some common symptoms include:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness upon standing up (orthostatic hypotension)
- Digestive problems, such as bloating, constipation, diarrhea, or nausea
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Bladder problems, such as urinary incontinence or difficulty emptying the bladder completely
- Sexual dysfunction, such as erectile dysfunction in men or vaginal dryness in women
- Sweating abnormalities, such as excessive sweating or a lack of sweating
The complications of Autonomic Neuropathy can be serious and even life-threatening. For example, orthostatic hypotension can increase the risk of falls and injuries, while digestive problems can lead to malnutrition and weight loss. Bladder problems can lead to urinary tract infections, and sexual dysfunction can affect a person’s quality of life.
Sexual Dysfunction
DPN can cause nerve damage that affects the nerves in the genital area, decreasing sexual function and satisfaction. In men with DPN, sexual dysfunction may manifest as erectile dysfunction, the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual activity.
Erectile dysfunction can be caused by nerve damage that affects blood flow to the penis. In women with DPN, sexual dysfunction may manifest as vaginal dryness, reduced sensation, or difficulty achieving orgasm. Sexual dysfunction can be caused by nerve damage that affects blood flow to the genital area or the ability to feel the sensation.
Hypoglycemia Unawareness
Hypoglycemia unawareness is a complication of diabetes in which a person’s blood sugar drops to dangerously low levels without them experiencing any symptoms. This can be particularly dangerous as the person may not realize that they need to take action to correct their blood sugar levels, which can lead to a loss of consciousness or seizures.
Hypoglycemia unawareness is more common in people with DPN because nerve damage can affect the body’s ability to detect low blood sugar levels. It can also occur in people who have had diabetes for a long time or frequently experience hypoglycemia episodes.
The symptoms of hypoglycemia typically include sweating, trembling, dizziness, and confusion. However, people with hypoglycemia unawareness may not experience any of these symptoms, making it difficult for them to know when their blood sugar is low.
Cardiovascular Complications
DPN can cause nerve damage that affects the blood vessels and the heart, leading to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and related complications. One of the primary cardiovascular complications of DPN is atherosclerosis, a condition in which the blood vessels become narrowed and hardened due to plaque buildup.
Atherosclerosis can increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. DPN can also affect the heart directly, causing damage to the heart muscle and reducing its ability to pump blood effectively.
High blood pressure is another common complication of DPN that can contribute to cardiovascular disease. High blood pressure can cause damage to the blood vessels and increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications.
Vision Problems
DPN can cause nerve damage that affects the eyes, leading to vision problems. One of the most common vision problems associated with DPN is diabetic retinopathy, a condition in which the blood vessels in the retina become damaged due to high blood sugar levels. Diabetic retinopathy can lead to vision loss and even blindness if left untreated. People with DPN are also at higher risk of developing cataracts and glaucoma, which can cause vision impairment or blindness.
Symptoms of vision problems associated with DPN can vary depending on the specific condition. Some common symptoms of diabetic retinopathy include blurry or distorted vision, floaters in the field of vision, and difficulty seeing at night. Cataracts can cause cloudy or blurry vision, while glaucoma can cause peripheral vision loss.
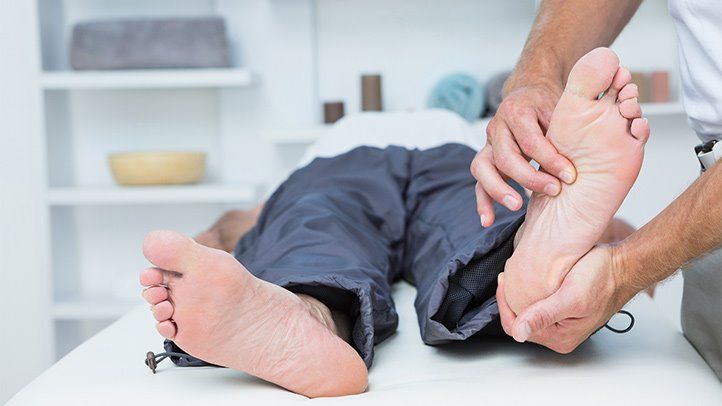

How Prevalent is DPN
DPN is a relatively common complication of diabetes, affecting up to 50% of individuals. It is most commonly diagnosed in individuals who have had diabetes for more than 25 years. The risk of developing Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy increases with age and is more common in individuals with poorly controlled diabetes.
The prevalence of DPN is higher in specific populations, such as those with type 2 diabetes, those with obesity, and those with high blood pressure. It is also more common in individuals who smoke and have high cholesterol levels. Men are also more likely to develop Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy than women.
The exact prevalence of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy is difficult to determine, as many individuals with the condition may not exhibit symptoms. However, it is estimated that up to 10% of individuals with diabetes have signs of DPN. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to increase globally, the prevalence of DPN will likely continue to rise.
How to Treat Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Here is a list of various ways to treat DPN:
- Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is critical in preventing and managing diabetic peripheral Neuropathy. Consistently monitoring and keeping blood sugar levels within a normal range can help slow the progression of nerve damage.
- Medications: Certain medications can help alleviate the pain associated with diabetic peripheral Neuropathy. Some examples include antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and opioids.
- Physical Therapy: Specific exercises and stretches can help improve strength and flexibility, decrease pain, and increase range of motion.
- Topical Treatments: Creams, lotions, and patches containing capsaicin, lidocaine, and other topical agents can help relieve pain and discomfort.
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): TENS uses low-voltage electrical current to relieve pain by stimulating the nerves in affected areas.
- Acupuncture: This alternative therapy involves the insertion of needles into specific points of the body to help reduce pain and promote healing.
- Massage Therapy: Massage can help relax muscles and reduce tension, which can help alleviate pain and improve overall comfort.
- Lifestyle Changes: Healthy lifestyle changes can help prevent and manage diabetic peripheral Neuropathy. Healthy lifestyle changes include maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and following a healthy diet.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on nerves or repair damaged nerves.
The most effective treatment plan will depend on the severity of the condition and the individual patient’s specific needs. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action.
How to Prevent DPN
Preventing DPN involves managing underlying diabetes and reducing the risk of complications. Here are some steps that may help prevent DPN:
- Control Blood Sugar Levels: Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is vital to preventing DPN. This can be achieved through healthy eating, regular physical activity, and taking diabetes medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- Manage Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: High blood pressure and cholesterol can increase the risk of DPN, so it is vital to monitor and manage these conditions through lifestyle changes and medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of DPN. Quitting smoking can help reduce this risk.
- Protect Feet: People with diabetes should take extra care to protect their feet from injury and infection. This includes wearing correctly fitting shoes, avoiding walking barefoot, and regularly checking feet for cuts, blisters, or other signs of damage.
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify and address any potential complications related to diabetes, including DPN.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: A healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, healthy eating, and stress management can help reduce the risk of DPN and other complications related to diabetes.
It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for managing diabetes and reducing the risk of complications such as DPN. By taking steps to manage diabetes and protect overall health, it may be possible to prevent or delay the onset of DPN.
Contact Information
If you’re ready to take charge of your health and embark on a journey toward a healthier, happier life, we invite you to contact us today. Our compassionate and knowledgeable staff is excited to take your call and help you on your health journey. We will work closely with you to develop a customized treatment plan that is right for you and provide the support and care you need every step of the way.
Don’t let health concerns hold you back – contact CoreMed Plus today and let us help you achieve optimal health and wellness. We look forward to hearing from you and helping you achieve a healthier, happier life.
- Email: [email protected]
- Phone: +1 248-666-6005


