Blood Work
At CoreMed Plus, we understand that blood work is an essential part of evaluating and maintaining a patient’s overall health. Our experienced medical team is dedicated to providing high-quality blood work services to our patients, focusing on accuracy, efficiency, and patient comfort. Whether you need blood work for routine check-ups, to monitor a chronic medical condition, or as part of cancer treatment, medication management, or pregnancy monitoring, we offer a wide range of blood work tests to meet your needs.
Our blood work services are designed to be comprehensive, providing patients with a complete evaluation of their overall health and identifying any potential risks or complications. We use state-of-the-art equipment and techniques to ensure the accuracy and reliability of our blood work results, and our team is highly trained in the latest diagnostic methods and procedures.
At CoreMed Plus, we understand that getting blood work done can be a stressful experience for some patients. That’s why we are committed to providing a comfortable and welcoming environment for all of our patients. Our medical team will take the time to explain the testing process and answer any questions you may have, and we will work with you to ensure that you feel comfortable and at ease throughout the testing process.
Our blood work services are designed to provide patients with the highest level of care and support, and we are dedicated to helping our patients achieve optimal health and wellness. Whether you need blood work for diagnostic purposes or as part of ongoing monitoring and care, we are here to provide the support and guidance you need to achieve your health goals.
What is Blood Work
Blood work, also known as a blood test, is a diagnostic test involving drawing a blood sample from a patient’s vein and analyzing it for various markers and substances. Blood work can be used to evaluate a wide range of medical conditions, as well as to monitor chronic conditions and assess overall health.
Blood work typically involves drawing blood from a vein in the arm using a needle and collecting the sample in a tube. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where it is tested for a variety of substances, including:
Blood Sugar: Blood work can be used to measure blood sugar levels, which can be useful in diagnosing and monitoring diabetes. High blood sugar levels may indicate diabetes, while low blood sugar levels may indicate hypoglycemia. Regular blood sugar monitoring can help patients with diabetes to manage their condition and prevent complications.
Cholesterol: Blood work can be used to measure cholesterol levels, which can be an important indicator of cardiovascular health. High levels of “bad” cholesterol (LDL) can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke, while high levels of “good” cholesterol (HDL) can lower the risk. If necessary, blood cholesterol levels can be managed through lifestyle changes and medication.
Kidney Function: Blood work can be used to evaluate kidney function by measuring creatinine levels and other substances in the blood. High levels of creatinine may indicate kidney damage or disease. Regular monitoring of kidney function can help healthcare providers detect and manage kidney disease and prevent complications.
Liver Function: Blood work can be used to evaluate liver function by measuring levels of enzymes and other substances in the blood. High levels of liver enzymes may indicate liver damage or disease. Regular monitoring of liver function can help healthcare providers detect and manage liver disease and prevent complications.
Blood Cell Counts: Blood work can be used to measure the number and types of blood cells in the body, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Abnormal blood cell counts may indicate anemia, infection, or other medical conditions. Regular blood cell monitoring can help healthcare providers detect and manage these conditions and prevent complications.
Hormone Levels: Blood work can be used to measure hormone levels, including thyroid hormones, sex hormones, and growth hormones. Hormone imbalances can cause various symptoms and medical conditions, including thyroid disorders, infertility, and growth disorders. Regular monitoring of hormone levels can help healthcare providers detect and manage these conditions and prevent complications.
Nutrient Levels: Blood work can be used to measure levels of various nutrients, including vitamins and minerals, to assess overall nutritional status. Nutrient deficiencies can cause various symptoms and medical conditions, including anemia, osteoporosis, and immune system dysfunction. Regular monitoring of nutrient levels can help healthcare providers detect and manage these deficiencies and prevent complications.
Blood work is a valuable diagnostic tool providing important information about a patient’s health. By analyzing various substances in the blood, healthcare providers can detect and monitor a wide range of medical conditions and evaluate overall health and nutritional status. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have questions or concerns about blood work or any other diagnostic tests.
Blood work can be used for a wide range of diagnostic purposes, including:
Screening for Medical Conditions: Blood work can be used to screen for medical conditions, such as diabetes, high cholesterol, or liver disease, in patients who may not have any symptoms. This type of blood work is often done as part of routine check-ups or as a part of health screenings for specific populations, such as people over 50 or those with a family history of certain medical conditions. Early detection of these conditions through blood work screening can lead to earlier treatment and improved outcomes.
Diagnosing Medical Conditions: Blood work can diagnose medical conditions, such as anemia, thyroid disease, or autoimmune disorders, by measuring levels of specific markers in the blood. Depending on the condition being tested for, blood work may involve measuring the levels of certain hormones, antibodies, or other substances in the blood. Accurate diagnosis through blood work can help healthcare providers develop an appropriate treatment plan and prevent complications.
Monitoring Chronic Medical Conditions: Blood work can be used to monitor chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, by measuring levels of specific markers in the blood over time. Regular blood work monitoring can help healthcare providers evaluate the effectiveness of treatment and make adjustments as needed. For example, blood work can be used to monitor blood sugar levels in patients with diabetes or cholesterol levels in patients with heart disease.
Assessing Overall Health: Blood work can be used to evaluate overall health and nutritional status by measuring levels of various nutrients and markers in the blood. This type of blood work can provide important information about a patient’s overall health, including potential deficiencies or imbalances in vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. Regular monitoring of nutrient levels can help healthcare providers detect and manage deficiencies and prevent complications.
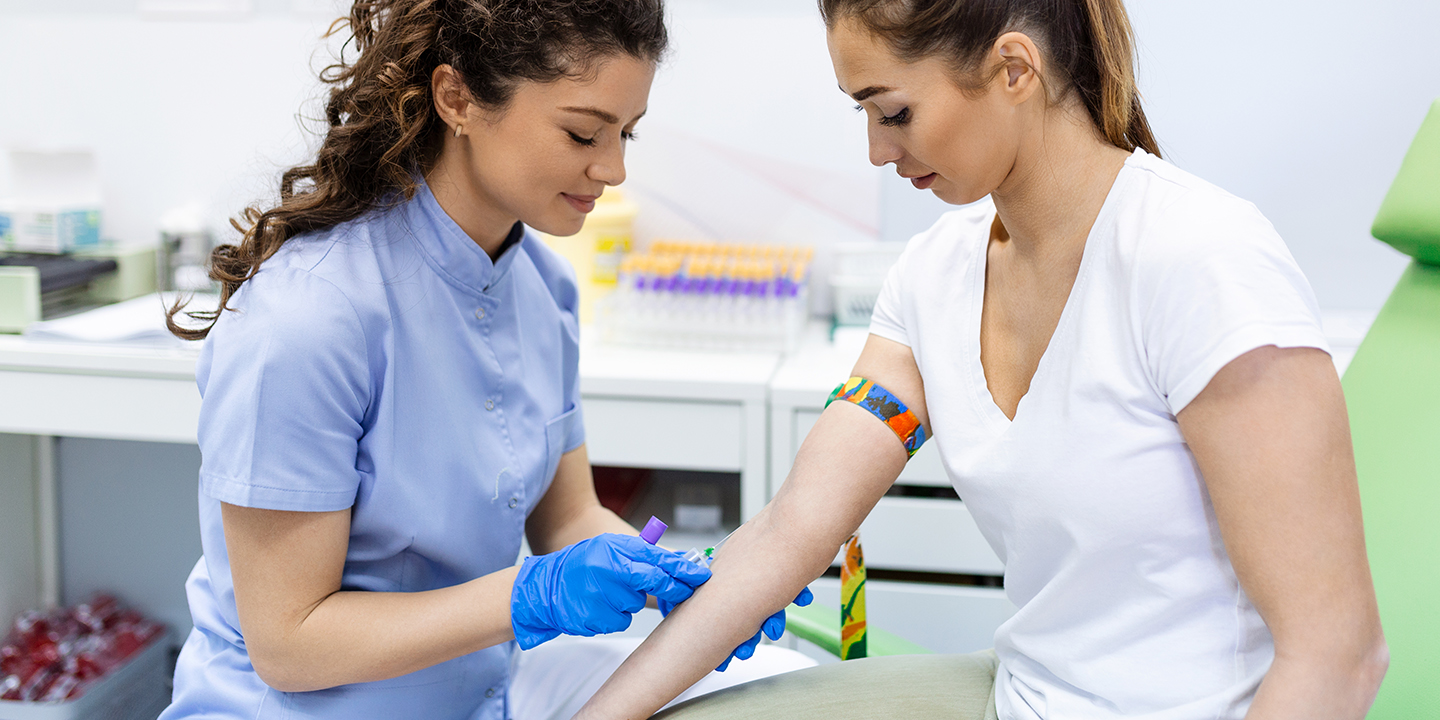

Why Someone Might Require Blood work
There are many reasons why someone might need blood work, including:
- Routine Check-Ups: Blood work can be used as part of routine check-ups to assess overall health and monitor for any changes in blood levels over time. This blood work is often done during annual physical exams or other routine healthcare visits. By measuring levels of various substances in the blood, healthcare providers can evaluate overall health and identify potential risks or changes in blood levels that may indicate a medical condition.
- Diagnostic Purposes: Blood work can diagnose medical conditions, such as anemia, thyroid disease, or autoimmune disorders, by measuring levels of specific markers in the blood. Depending on the condition being tested for, blood work may involve measuring the levels of certain hormones, antibodies, or other substances in the blood. Accurate diagnosis through blood work can help healthcare providers develop an appropriate treatment plan and prevent complications.
- Screening for Medical Conditions: Blood work can be used to screen for medical conditions, such as diabetes, high cholesterol, or liver disease, in patients who may not have any symptoms. This type of blood work is often done as part of routine check-ups or as a part of health screenings for certain populations, such as people over 50 or those with a family history of certain medical conditions. Early detection of these conditions through blood work screening can lead to earlier treatment and improved outcomes.
- Monitoring Chronic Medical Conditions: Blood work can be used to monitor chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, by measuring levels of specific markers in the blood over time. Regular blood work monitoring can help healthcare providers evaluate the effectiveness of treatment and make adjustments as needed. For example, blood work can be used to monitor blood sugar levels in patients with diabetes or cholesterol levels in patients with heart disease.
- Pre-Surgical Evaluation: Blood work is often done before surgery to evaluate a patient’s health and identify potential risks or complications. This type of blood work may involve measuring levels of specific substances in the blood that can indicate an increased risk of bleeding or other complications during surgery. By identifying these risks early on, healthcare providers can take steps to minimize the risk of complications during and after surgery.
- Medication Management: Blood work may be used to monitor levels of certain medications in the blood, to ensure that patients receive the appropriate dose. Depending on the medication being monitored, blood work may involve measuring levels of the medication itself or certain substances in the blood that can indicate how the body is processing the medication. By monitoring medication levels, healthcare providers can ensure patients receive the appropriate dose and adjust medication as needed to optimize treatment.
Continual blood work monitoring may be necessary for a variety of reasons, including:
- Chronic Medical Conditions: Patients with chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes or kidney disease, may require regular blood work to monitor disease progression and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. This type of blood work can help healthcare providers identify changes in blood levels that may indicate a worsening of the condition or a need to adjust treatment. Healthcare providers can optimize treatment and prevent complications by monitoring blood levels over time.
- Medication Management: Patients taking certain medications, such as blood thinners or chemotherapy drugs, may require regular blood work to monitor levels of the medication in the blood and adjust doses as needed. This type of blood work can help healthcare providers ensure that patients are receiving the appropriate dose of medication and adjust treatment as needed to prevent side effects or other complications.
- Recovery From Illness or Injury: Patients recovering from a serious illness or injury may require regular blood work to monitor their recovery and ensure that their body is healing properly. This type of blood work can help healthcare providers evaluate the effectiveness of treatment and identify any complications or risks to recovery. By monitoring blood levels over time, healthcare providers can adjust treatment as needed and ensure a successful recovery.
- Cancer Treatment: Patients undergoing cancer treatment, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, may require regular blood work to monitor their response to treatment and detect any side effects or complications. This type of blood work can help healthcare providers adjust treatment as needed and prevent serious complications, such as infections or bleeding.
- Pregnancy: Pregnant women may require regular blood work to monitor their health and the health of their developing baby. This type of blood work can help healthcare providers identify any potential risks or complications, such as gestational diabetes or preeclampsia, and take steps to prevent or manage these conditions. Healthcare providers can ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery by monitoring blood levels over time.
In many cases, blood work can provide valuable information about a patient’s health and help healthcare providers to make an accurate diagnosis and develop an effective treatment plan. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have questions or concerns about blood work or any other diagnostic tests.
Why Choose CoreMed Plus
You should choose CoreMed Plus for your blood work needs for many reasons. Here are just a few:
- Expertise: Our medical team is highly trained and experienced in blood work procedures and techniques, and we use the latest equipment and methods to ensure accurate and reliable results.
- Convenience: We understand that getting blood work done can be time-consuming and stressful. We offer flexible scheduling options and efficient testing procedures to minimize wait times and help you get back to your day quickly.
- Comfort: We strive to create a welcoming and comfortable environment for all of our patients, and our medical team will work closely with you to ensure that you feel relaxed and at ease throughout the testing process.
- Comprehensive Testing: We offer a wide range of blood work tests for both diagnostic and monitoring purposes, including tests for blood sugar, cholesterol, kidney function, liver function, blood cell counts, hormone levels, and nutrient levels.
- Personalized Care: Every patient deserves personalized care and attention at Core Med Plus. Our medical team will work closely with you to develop a testing plan that meets your unique needs and health goals.
- Results: Our medical team will review your blood work results in detail, helping you understand what the results mean and what steps you can take to improve your health and wellness.
At CoreMed Plus, we are committed to providing our patients with the highest level of care and support for all their blood work needs. If you’re looking for a reliable and trusted provider for your blood work testing, we are here to help.
Contact Information
If you’re ready to take charge of your health and embark on a journey toward a healthier, happier life, we invite you to contact us today. Our compassionate and knowledgeable staff is excited to take your call and help you on your health journey. We will work closely with you to develop a customized treatment plan that is right for you and provide the support and care you need every step of the way.
Don’t let health concerns hold you back – contact CoreMed Plus today and let us help you achieve optimal health and wellness. We look forward to hearing from you and helping you achieve a healthier, happier life.
- Email: [email protected]
- Phone: +1 248-666-6005


