Arthritis
Arthritis is a common condition affecting millions of people worldwide, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced joint mobility. There are many different types of arthritis, each with its causes, symptoms, and treatments. At CoreMed Plus, we understand the challenges and complexities of managing arthritis and are committed to providing personalized, patient-centered care to individuals with arthritis.
At CoreMed Plus, we offer various services to help manage arthritis, including diagnostic testing, medication management, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Our healthcare team works closely with each patient to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses their unique needs and goals. We believe in a comprehensive approach to arthritis management that includes medical care, social support, caregiver education, and ongoing monitoring and adjustment of treatment plans as needed.
Our healthcare team at CoreMed Plus includes board-certified physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, physical therapists, and other healthcare professionals who are experts in the management of arthritis. We stay up-to-date on the latest advances in arthritis research and treatment, and we are committed to providing the highest quality care to our patients.
If you are experiencing joint pain, stiffness, or reduced mobility, it is vital to seek medical care. Early diagnosis and treatment of arthritis can help manage symptoms and prevent further damage to the joints. At CoreMed Plus, we help you manage your arthritis and improve your quality of life.
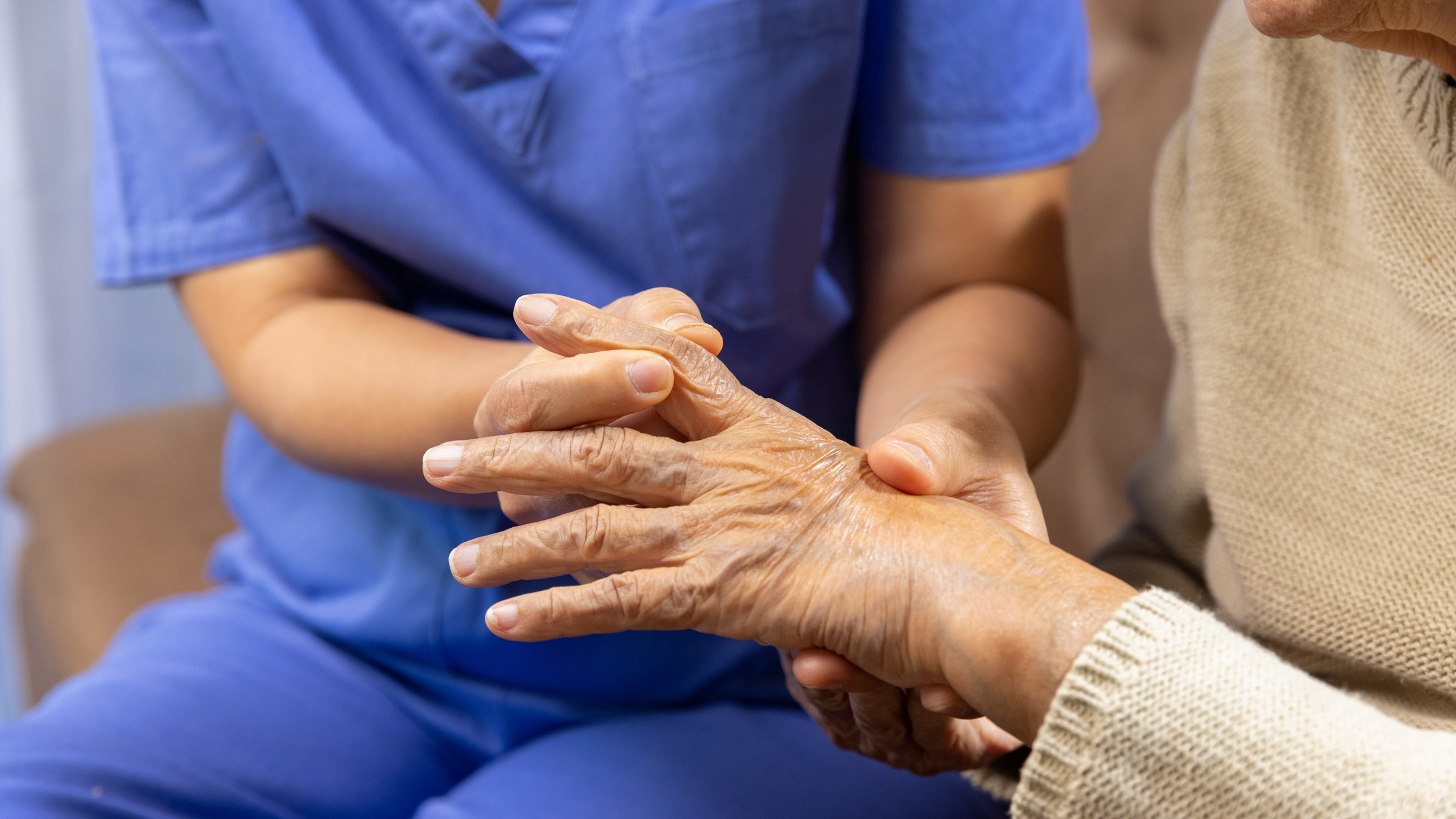

What is Arthritis
Arthritis is a general term used to describe inflammation of the joints. It is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide and can occur in people of all ages, genders, and ethnicities. Arthritis can cause pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced range of motion in affected joints and can affect one or multiple joints in the body.
Types of Arthritis
There are many different types of arthritis, each with its own causes, symptoms, and treatments. Some of the most common types of arthritis include:
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common joint disorder that occurs when the protective cartilage cushions the ends of bones wears down over time, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the affected joint. OA can occur in any joint but is most commonly found in the hands, hips, knees, and spine.
The exact cause of OA is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Some of the factors that may contribute to the development of OA include:
- Aging: As people age, the cartilage in their joints can naturally wear down, leading to OA.
- Genetics: There is evidence that some people may be more genetically susceptible to developing OA.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing OA, particularly in the knees.
- Joint Injuries: Injuries to a joint, such as a fracture or ligament tear, can increase the risk of developing OA in that joint.
The symptoms of OA can vary widely from person to person and may include:
- Joint Pain and Stiffness: OA can cause pain and stiffness in the affected joint, particularly after periods of inactivity or overuse.
- Swollen Joints: OA can cause joint swelling, particularly in the fingers and knees.
- Reduced Range of Motion: OA can cause a reduction in joint mobility and flexibility.
- Joint Creaking or Cracking: Some people with OA may experience joint creaking or cracking sounds.
Diagnosis of OA typically involves a physical exam, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI. Treatment of OA typically consists of a combination of medications and lifestyle modifications.
Some of the medications used to treat OA include:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These medications can help reduce pain and inflammation in affected joints.
- Acetaminophen: This medication can help manage pain but does not have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Topical Treatments: Creams or gels that contain NSAIDs can be applied directly to the affected joint to reduce pain and inflammation.
In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms of OA. These may include:
- Regular Exercise: Regular exercise can help improve joint mobility and reduce pain and stiffness.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce joint stress.
- Assistive Devices: Using assistive devices, such as braces or canes, can help support affected joints and improve mobility.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve joint strength and flexibility and teach exercises and techniques to manage symptoms.
OA is a chronic condition that can cause joint pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. With appropriate medical care and lifestyle modifications, many people with OA can manage their symptoms effectively and lead active and fulfilling lives.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder that causes joint inflammation, resulting in pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced range of motion. The condition can also affect other body parts, such as the lungs, heart, and blood vessels. RA affects about 1% of the population and is more common in women than men.
The exact cause of RA is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. In RA, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues in the joints, causing inflammation and damage to the joints and surrounding tissues.
The symptoms of RA typically develop gradually and can be mild at first. Common symptoms of RA may include:
- Joint Pain and Stiffness: RA typically affects the small joints in the hands and feet first but can progress to other joints.
- Swollen Joints: RA can cause joint swelling, particularly in the fingers and toes.
- Fatigue: Many people with RA experience fatigue, which can be severe and affect daily activities.
- Joint Deformity: RA can cause joint deformity over time, particularly in the hands and feet.
- Loss of Mobility: RA can cause joint damage and loss of mobility, mainly if the condition is not managed effectively.
Diagnosis of RA typically involves a physical exam, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI. Treatment of RA typically consists of a combination of medications and lifestyle modifications.
Some of the medications used to treat RA include:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These medications can help reduce pain and inflammation in affected joints.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): These medications can help slow the progression of joint damage and reduce inflammation.
- Biologic Drugs: These medications target specific components of the immune system to reduce inflammation and slow joint damage.
In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms of RA. These may include:
- Regular Exercise: Exercise can help improve joint mobility and reduce pain and stiffness.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce stress on the joints.
- Stress Reduction: Stress can exacerbate symptoms of RA, so stress reduction techniques such as meditation or yoga may be helpful.
- Assistive Devices: Using assistive devices, such as braces or splints, can help support affected joints and improve mobility.
RA is a chronic condition that can cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. With appropriate medical care and lifestyle modifications, many people with RA can manage their symptoms effectively and lead active and fulfilling lives. Early diagnosis and treatment of RA are essential to slow the progression of joint damage and improve long-term outcomes.
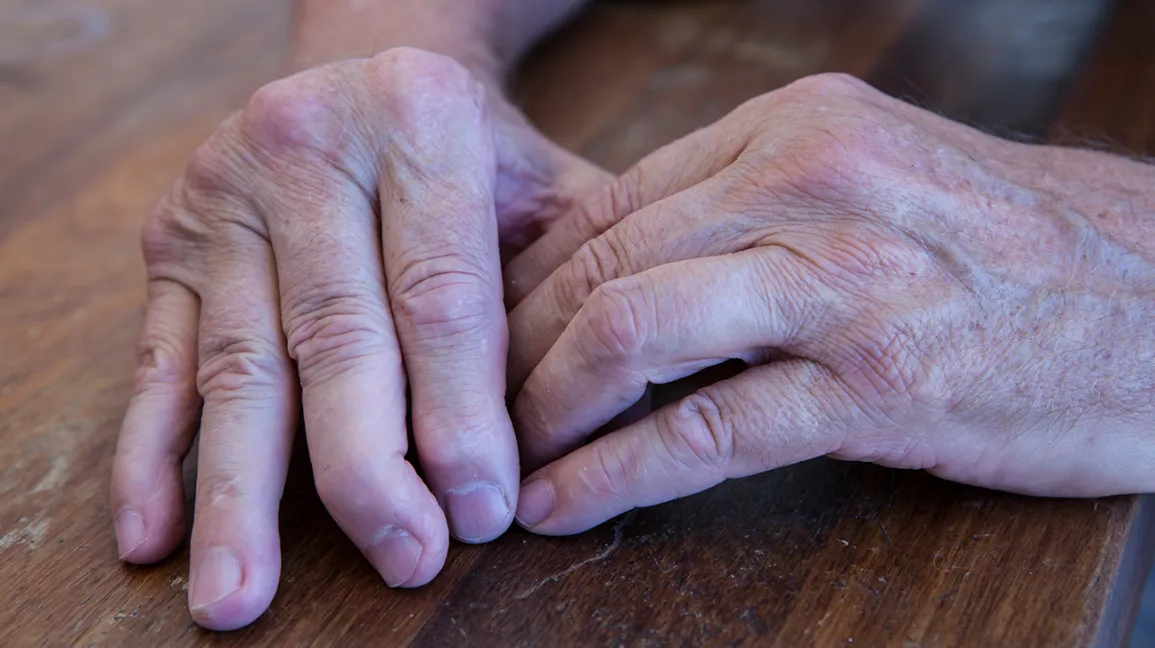
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory arthritis that occurs in some people with psoriasis, a chronic skin condition that causes red, scaly patches. Psoriatic arthritis can cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling and affect any joint. The condition is believed to be caused by an autoimmune reaction in which the body’s immune system attacks healthy cells and tissues in the joints.
Psoriatic arthritis can occur in people of all ages, genders, and ethnicities and may be more common in people with a family history. The symptoms of psoriatic arthritis can vary widely from person to person and may include:
- Joint Pain and Stiffness: Psoriatic arthritis can cause pain and stiffness in the joints, particularly in the fingers, toes, and lower back.
- Swollen Joints: Psoriatic arthritis can cause joint swelling, particularly in the fingers and toes.
- Fatigue: Many people with psoriatic arthritis experience fatigue, which can be severe and affect daily activities.
- Skin Changes: Psoriatic arthritis can cause changes in the skin, including red, scaly patches or nail changes.
- Eye Inflammation: In some cases, psoriatic arthritis can cause inflammation in the eyes, which can cause eye pain and vision problems.
Diagnosing psoriatic arthritis typically involves a physical exam, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI. Treatment of psoriatic arthritis typically consists of a combination of medications and lifestyle modifications.
Some of the medications used to treat psoriatic arthritis include:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These medications can help reduce pain and inflammation in affected joints.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): These medications can help slow the progression of joint damage and reduce inflammation.
- Biologic Drugs: These medications target specific immune system components to reduce inflammation and slow joint damage.
In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms of psoriatic arthritis. These may include:
- Regular Exercise: Exercise can help improve joint mobility and reduce pain and stiffness.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce stress on the joints.
- Stress Reduction: Stress can exacerbate symptoms of psoriatic arthritis, so stress reduction techniques such as meditation or yoga may be helpful.
Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic condition that can cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. With appropriate medical care and lifestyle modifications, many people with psoriatic arthritis can manage their symptoms effectively and lead active and fulfilling lives.
Gout
Gout is a type of arthritis that occurs when there is excessive uric acid in the body, leading to the formation of urate crystals in the joints. The condition can cause sudden, severe pain, swelling, and redness in affected joints, most commonly the joint at the base of the big toe. Gout affects an estimated 4% of adults in the United States and is more common in men than women.
The exact cause of gout is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and dietary factors. Some of the factors that may contribute to the development of gout include:
- Diet: Eating a diet high in purines, a compound found in certain foods such as red meat, organ meats, seafood, and alcohol, can increase the risk of gout.
- Genetics: Gout tends to run in families, suggesting that there may be a genetic component to the condition.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, kidney disease, and diabetes, can increase the risk of developing gout.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics and aspirin, can increase the risk of developing gout.
The symptoms of gout typically develop suddenly and can be very painful. The most common gout symptom is a pain in the joint at the base of the big toe, which may be accompanied by swelling, redness, and warmth. Other symptoms of gout may include fever, chills, and fatigue.
Diagnosis of gout typically involves a physical exam and medical history, as well as tests to measure uric acid levels in the blood and joint fluid. Treatment of gout typically involves medications to manage pain and inflammation and lifestyle modifications to reduce the risk of future gout attacks.
Some of the medications used to treat gout include:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These medications, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, can help reduce pain and inflammation in affected joints.
- Colchicine: This medication can help reduce inflammation and pain during a gout attack.
- Corticosteroids: These medications can be taken orally or injected into affected joints to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Urate-Lowering Medications: These medications, such as allopurinol and febuxostat, can help lower the levels of uric acid in the blood and reduce the risk of future gout attacks.
In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications can help reduce the risk of gout attacks. These may include:
- Limiting intake of foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, and seafood.
- Limiting intake of alcohol, particularly beer.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Drinking plenty of fluids, particularly water.
- Engaging in regular physical activity.
Gout is a painful and sometimes debilitating condition that can be managed with appropriate medical care and lifestyle modifications. It is important to seek medical care if you experience gout symptoms, as early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of future gout attacks. With proper care and management, many people with gout can lead active and fulfilling lives.
Many treatments are available for arthritis, depending on the type and severity of the condition. Treatment may include medications to reduce inflammation and pain, physical therapy to improve joint function and mobility, and lifestyle modifications such as weight loss, exercise, and dietary changes. Surgery may sometimes be recommended to repair or replace damaged joints.
It is essential to seek medical care if you experience joint pain, stiffness, or swelling, as early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent further damage to the joints. With proper care and management, many people with arthritis can lead active and fulfilling lives.

CoreMed Plus Are the Doctors You Can Trust
At CoreMed Plus, we are passionate about providing the highest quality care to individuals with arthritis. Our healthcare team is dedicated to helping our patients manage their symptoms, improve mobility, and lead active and fulfilling lives. We understand the impact that arthritis can have on daily life, and we are committed to providing personalized, patient-centered care to each individual we serve.
With our comprehensive approach to arthritis management, we offer a range of services tailored to each patient’s unique needs and goals. From diagnostic testing to medication management, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications, we are here to help our patients every step of the way. We believe in the power of a multidisciplinary approach to care, and we work closely with our patients to develop an effective, sustainable, and empowering treatment plan.
At CoreMed Plus, we proudly offer world-class care to individuals with arthritis. Whether you are living with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, or another form of the condition, we are here to help you manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. If you are looking for compassionate, expert care for arthritis, we invite you to contact us today to schedule a consultation.
Contact Information
If you’re ready to take charge of your health and embark on a journey toward a healthier, happier life, we invite you to contact us today. Our compassionate and knowledgeable staff is excited to take your call and help you on your health journey. We will work closely with you to develop a customized treatment plan that is right for you and provide the support and care you need every step of the way.
Don’t let health concerns hold you back – contact CoreMed Plus today and let us help you achieve optimal health and wellness. We look forward to hearing from you and helping you achieve a healthier, happier life.
- Email: frontdesk@coremedplus.com
- Phone: +1 248-666-6005


